Belatacept in kidney transplantation – past and future perspectives.
Authors:
Siddiqui Z, Tedesco-Silva H, Riella LV.
Abstract
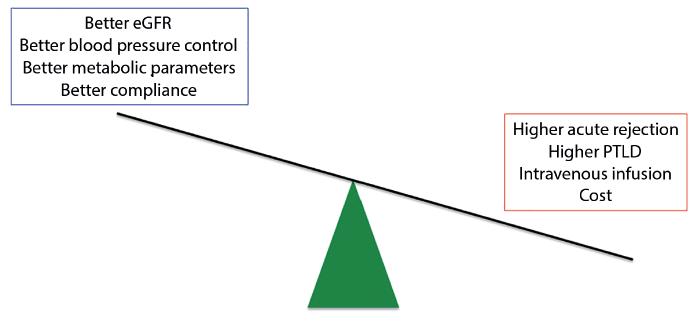
Calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs) are used widely for maintenance immunosuppression in renal transplant recipients. However, their side effect profile has led researchers to attempt to find safer alternatives that can maintain effective long-term immunosuppression with less toxicity. Belatacept is a CTLA4-Ig molecule designed to block the costimulatory B7-CD28 signal needed for activation of effector T cells. While it has shown great promise in clinical trials, it has made halting progress towards replacing CNIs in actual clinical practice. The BENEFIT trial revealed some of the advantages of belatacept in terms of maintaining renal function after transplant and reducing some of the metabolic side effects of CNIs related to hypertension and dyslipidemia. Despite that, some cautionary signals have emerged as well, in that belatacept-treated patients experience higher acute rejection rates and greater risk for PTLD. Furthermore, the requirement for monthly intravenous infusions has presented logistical and cost challenges for widespread adoption.
J Bras Nefrol. 2017 Apr-Jun;39(2):205-212.
Figure
Advantageous and disadvantages of belatacept use in kidney transplantation.