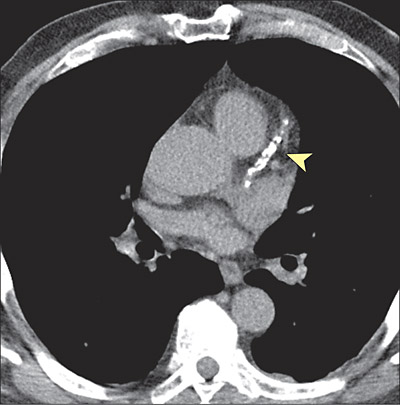
The coronary artery calcium (CAC) score is a widely recognized
surrogate marker of coronary atherosclerosis, and its presence and
extent are associated with increased risk of incident cardiovascular
events and mortality [1]. In fact, CAC provides the most valuable
incremental value to predict future cardiovascular events beyond
clinical risk factors [2,3]. The prognostic value of CAC has been
validated in diverse populations across a wide spectrum of age,
gender, racial and ethnic background [1,4]. Additionally, the value
of CAC has also been extended to higher risk individuals, such as
diabetics [5] or those with chronic kidney disease (CKD) [6]…
…
Bittencourt MS, Riella LV.