Abstract:
The kidney is a vital organ that regulates the bodily fluid and electrolyte homeostasis via tailored urinary excretion. Kidney injuries that cause severe or progressive chronic kidney disease have driven the growing population of patients with end-stage kidney disease, leading to substantial patient morbidity and mortality. This irreversible kidney damage has also created a huge socioeconomical burden on the healthcare system, highlighting the need for novel translational research models for progressive kidney diseases. Conventional research methods such as in vitro 2D cell culture or animal models do not fully recapitulate complex human kidney diseases. By contrast, directed differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells enables in vitro generation of patient-specific 3D kidney organoids, which can be used to model acute or chronic forms of hereditary, developmental, and metabolic kidney diseases. Furthermore, when combined with biofabrication techniques, organoids can be used as building blocks to construct vascularized kidney tissues mimicking their in vivo counterpart. By applying gene editing technology, organoid building blocks may be modified to minimize the process of immune rejection in kidney transplant recipients. In the foreseeable future, the universal kidney organoids derived from HLA-edited/deleted induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) lines may enable the supply of bioengineered organotypic kidney structures that are immune-compatible for the majority of the world population. Here, we summarize recent advances in kidney organoid research coupled with novel technologies such as organoids-on-chip and biofabrication of 3D kidney tissues providing convenient platforms for high-throughput drug screening, disease modelling, and therapeutic applications.
Download PDF here.
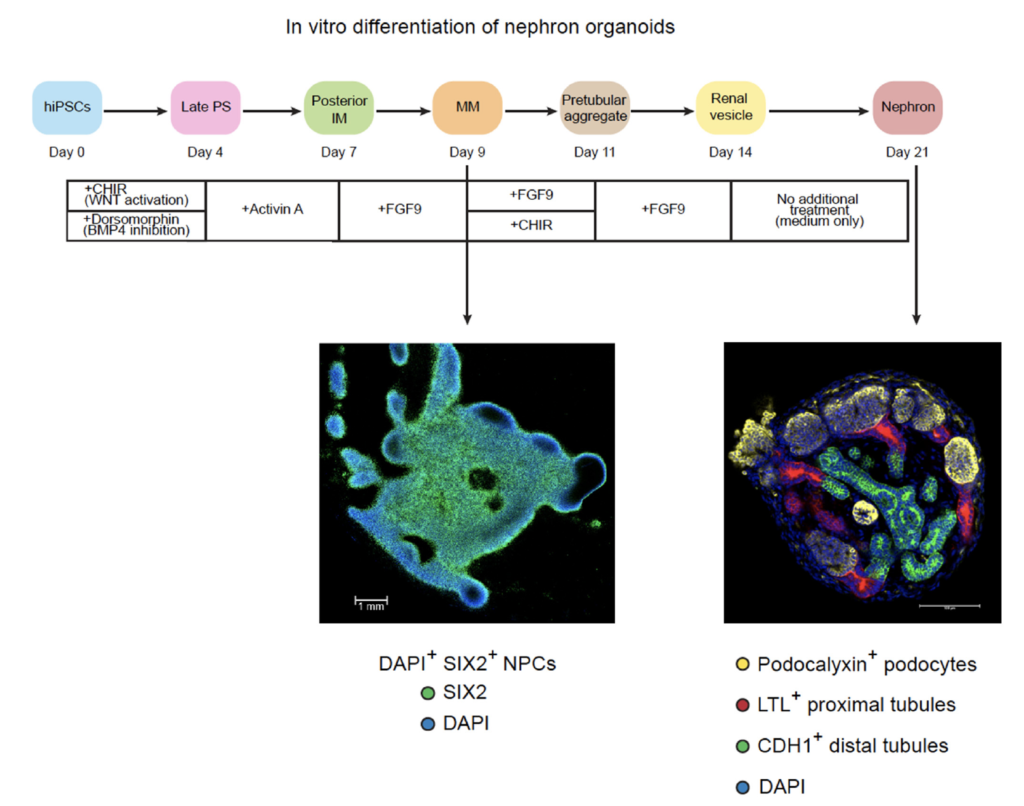
Figure. Directed differentiation of kidney organoids.