Front Med. 2020 Jul 21;7:423.
Authors
Benedetti C, Waldman M, Zaza G, Riella LV, Cravedi P.
Abstract
The new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has become a world health emergency. The disease predominantly effects individuals between 30 and 79 years of age with 81% of cases being classified as mild. Despite the majority of the general population displaying symptoms similar to the common cold, COVID-19 has also induced alveolar damage resulting in progressive respiratory failure with fatalities noted in 6.4% of cases. Direct viral injury, uncontrolled inflammation, activation of coagulation, and complement cascades are thought to participate in disease pathogenesis. Patients with COVID-19 have displayed kidney damage through acute kidney injury, mild proteinuria, hematuria, or slight elevation in creatinine possibly as consequence of kidney tropism of the virus and multiorgan failure. The impact of COVID-19 on patients with pre-existing kidney impairment, including those with chronic kidney disease, kidney transplant recipients, and individuals on hemodialysis (HD) has not yet been clearly established. No specific treatments for COVID-19 have been found yet. Research has revealed several agents that may have potential efficacy against COVID-19, and many of these molecules have demonstrated preliminary efficacy against COVID-19 and are currently being tested in clinical trials.
Link to article
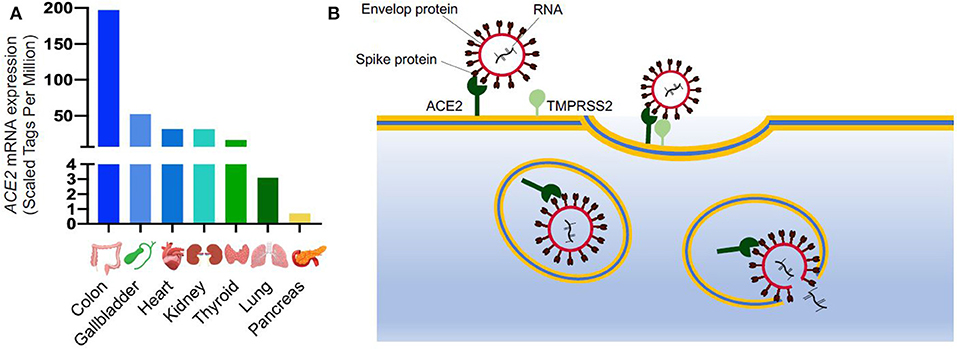 Figure: SARS-CoV-2 entry into the cells. (A) ACE2 mRNA expression in different organs from FANTOM5 dataset (11); (B) Schematic of SARS-CoV-2 entry into the cells. ACE2 is expressed on cell surface and it is recognized by the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. After binding to ACE2, the viral spike glycoprotein is primed by a host serine protease (TMPRSS2), which allows internalization by endocytosis. Once inside the cells, SARS-CoV-2 replicates utilizing the cellular transcriptional machinery. ACE2, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2; SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2; TMPRSS2, Transmembrane Serine Protease 2.
Figure: SARS-CoV-2 entry into the cells. (A) ACE2 mRNA expression in different organs from FANTOM5 dataset (11); (B) Schematic of SARS-CoV-2 entry into the cells. ACE2 is expressed on cell surface and it is recognized by the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. After binding to ACE2, the viral spike glycoprotein is primed by a host serine protease (TMPRSS2), which allows internalization by endocytosis. Once inside the cells, SARS-CoV-2 replicates utilizing the cellular transcriptional machinery. ACE2, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2; SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2; TMPRSS2, Transmembrane Serine Protease 2.
