Abstract:
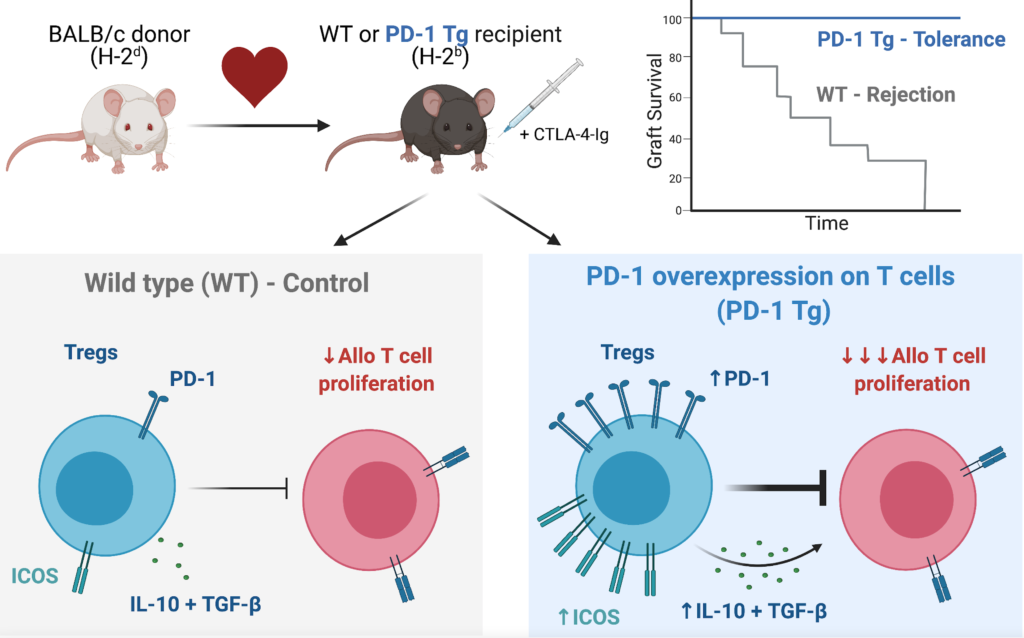
The PD-1: PD-L1 is a potent inhibitory pathway involved in immune regulation and a potential therapeutic target in transplantation. In this study, we show that overexpression of PD-1 (PD-1 Tg) on T cells promotes allograft tolerance in a fully MHC-mismatched cardiac transplant model when combined with costimulation blockade (CTLA-4-Ig). PD-1 overexpression on T cells also protected against chronic rejection in a single MHC II mismatched cardiac transplant model, while it still allowed the generation of an effective immune response against an Influenza A virus. Notably, Treg cells from PD-1 Tg mice were required for tolerance induction and presented higher ICOS expression than those from wild-type mice. Survival benefit of PD-1 Tg recipients required ICOS signaling and donor PD-L1 expression. These results indicate that modulation of PD-1 expression, in combination with a costimulation blockade, is a promising therapeutic target to promote transplant tolerance.